Blockchain technology feels both incredibly new and like it has always been around, but do you know how when it was actually created? And by whom?
Looking on the internet gives a variety of answers, not least because it’s not easy to pin down the exact moment when blockchain was born.
So in this article, we’re taking a look at the evolution of blockchain technology, from its earliest incarnations to what the future holds.
The evolution of blockchain technology: its creation and the early years
The very start of the blockchain history timeline goes as far back as 1979 when Ralph Merkle’s Merkle Tree was introduced, developing a data structure for public key distribution and digital signatures and patenting it as ‘tree authentication’.
Another critical step towards blockchain happened three years later with a dissertation by David Chaum that had most of the elements that make up blockchain.
In 1991, an article by Stuart Haber and W. Scott Stornetta described a cryptographically secured chain of blocks with the goal of preventing users from backdating or forward-dating electronic documents.
Other people played a part in the gradual development of ideas that would turn into what we know today, but who invented blockchain, and who created cryptocurrency? The answer to both is Satoshi Nakamoto, though it’s an answer that leads to more questions.
Nakamoto is a pseudonym for one or more programmers who may come from Japan, the USA, or Europe. In 2008 he published a document called Bitcoin: A Peer-To-Peer Electronic Cash System, following it up a year later with the implementation of the first blockchain.
The first transaction took place when Nakamoto sent an associate the first ten bitcoins. He remained involved the the continued development of blockchain until 2010 before handing over the source code, network key and domains and walking away.
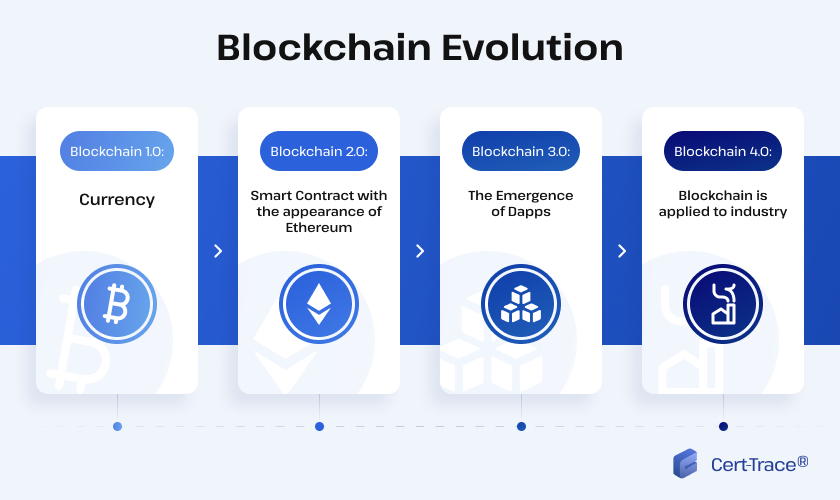
Phases of blockchain evolution
That’s how it came to exist but there has been a significant amount of evolution of blockchain technology in the years since 2009. In this next section, we’ll cover how blockchain evolution has happened and what the impact has been, from bitcoin to Ethereum to NFT and beyond.
1. Bitcoin and blockchain
Blockchain and bitcoin were invented together by the same person (or persons) so it’s inevitable that they were strongly linked together in the early years. Nakamoto invented both to improve on issues he had identified with traditional finance by removing third-party intermediaries by decentralizing the transaction process.
And blockchain transactions were the key element of this initial phase, from its creation in January 2009 to the start of online forums and the first bitcoin exchange (Bitcoin Market) being launched in October of the same year.
Another key milestone had happened in between, with Laszlo Hanyecz paying 10,000 bitcoin for two pizzas on May 22nd, marking the first commercial bitcoin transaction.
2. Ethereum Development
If blockchain had continued to be simply connected to transactions, it would still be one of the most important technological developments of the 21st Century. However, from the very earliest theories that led to its creation, there has always been the potential for it to play a much wider role in society.
In November 2013, Vitalik Buterin published a white paper introducing Ethereum, focusing more on smart contracts than transactions. Much like how bitcoin removed the need for a third party in financial transactions, smart contracts decentralized the way digital agreements could take place thanks to a set of rules hard-coded into Ethereum’s blockchain.
Ethereum is a blockchain-based computing program and its introduction has been called the second most important development in this area after the creation of bitcoin, and while it still offers a currency of its own (ether), its ability to store and operate computer code has been the real game-changer.
3. Blockchain 3.0
The development of Ethereum has been called blockchain 2.0 because of its transformative effect, enabling the creation of decentralized applications. However, it wasn’t without its limitations, particularly when it came to scalability, but these have largely been resolved by the arrival of blockchain 3.0.
The major step forward in this area has been a new consensus algorithm known as proof-of-stake, which replaces block mining with transaction validation, speeding up the process. This is especially the case in networks with more and more validators, helping those networks to scale up more quickly.
Blockchain 3.0 has also helped solve issues with interoperability that were caused when blockchains were siloed away from each other, making it difficult to convert from one to another. Bridges have been introduced that connect networks, making it much easier to switch and convert.
4. Hyperledger
While blockchain has largely been created by individuals rather than corporations, hyperledger is an example of bigger businesses getting involved. It was created in 2016 by the Linux Foundation and has had contributions from the likes of IBM, Samsung, Intel, Microsoft and others.
However, it remains an open-source project and is used to support the development of blockchain-based ledgers, creating frameworks, standards and libraries and acting as a hub for them. It can be used to improve the efficiency and performance of these frameworks and libraries and their transactions.
5. EOS IO
A year after hyperledger, blockchain took another step forward in 2017 with the introduction of EOS IO, a smart contract platform to support commercial decentralized applications and eliminate transaction fees. It can also conduct millions of transactions per second.
6. NFT
One of the most publicly famous (or infamous) aspects of blockchain has been non-fungible tokens (NFTs), unique digital identifiers that can be recorded on a blockchain to certify ownership. This allowed them to be used commercially to sell digital art, in-game assets, music and films.
This helped NFTs break into the mainstream in ways that other blockchain developments had not yet done, with major artists utilizing them, but legal issues with copyright, fraud and pyramid schemes have seen a backlash and decline in their usage in recent years.
The future of blockchain technology
The NFT bubble may have burst but the future remains bright as new emerging blockchain trends find ways to utilize it more and more aspects of our everyday life. Its smart contracts, transactions and applications have the potential to be used by both businesses and individuals, particularly when it comes to cloud computing.
The market for blockchain is expected to grow to over $39 billion by 2025 and we will continue to see blockchain disrupt and revolutionize the global banking systems in years to come. It also has an important role to play in cybersecurity, supply chain management, healthcare and even politics, where it has the potential to resolve issues with voter fraud.
Conclusion
So, this has been the evolution of blockchain technology up to this point. As you can see, it has come a long way thanks to the innovations and efforts of developers around the world and the potential to go much further in the future.
To find out more about how Cert-Trace® will be a part of this ongoing revolution get in touch at info@tracert.digital.
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
Average rating 5 / 5. Vote count: 541
No votes so far! Be the first to rate this post.


